General Firewall setup:The MI Listener can be decided by selection through Admin Site in Performance Center. This selection does not need to be changed generally.
Note: If Controller and MI Listener are on different machines, then port 50500 needs to be opened between Controller and MI Listener machines.
Steps to setup monitor/running Vuser over firewall:General Setup steps:Shut down LoadRunner programs (controller, agent…) before the setup. For this, you may need to kill processes magentservice.exe and wlrun.exe through Task Manager -> Processes (as shown below).
Setup on Over the Firewall Agent (Load Generator machine):
a. Go to agent machine (Load Generator machine).
b. Click Start –> Programs -> Mercury Performance Center -> Advanced Settings -> Agent Configuration
c. Check the options Enable Firewall Agent and Enable Terminal Services.
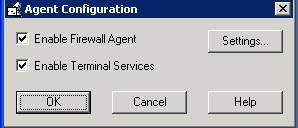
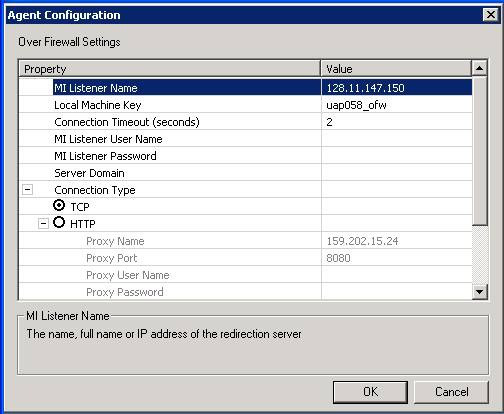 d. Click Settings button.
d. Click Settings button.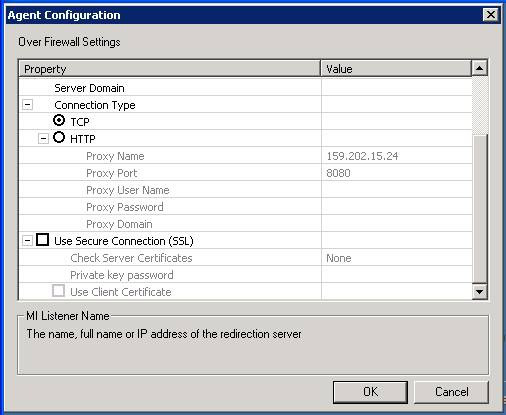
i. Set MI Listener Name to IP of MI listener machine.
ii. Set Local Machine Key to a symbolic identifier. For example, uap058_ofw.
e. To start the Performance Center agent as service, go to Command prompt and go to F:Program FilesMercuryPerformance Centerlaunch_servicebin folder in Load Generator machine (the drive may be different depending on, in which drive the Mercury Performance Center was installed. Now, run following commands in Command prompt.
To stop LoadRunner agent as service:
To stop LoadRunner agent as service:
magentservice.exe – remove
To start LoadRunner agent as service:
magentservice.exe – install
To stop LoadRunner agent as process:
magentproc.exe – remove
To start LoadRunner agent as process:
magentproc.exe – install
Note:(1) Make sure that Performance Center Agent is running by "Local System Account" (select the radio button as shown below after going to Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services -> Right Click on “Performance Center Agent” -> Click on “Log On” and then stop/start the service again from there).
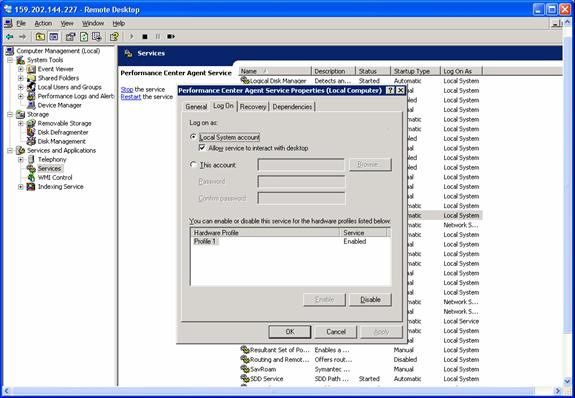
(2) Make sure that the Performance Center Agent runs as Service only, so that once you logout of the Load generator machine, the LoadRunner Agent should still continue running. Also, it should be set to run as “Automatic”, so that when Load Generator machine goes down, then the Performance Center Agent should run automatically, once the machine is up. This can be verified by checking “Performance Center Agent Service” in Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services. It also shows whether the Agent Service is started/running. An alternative way to see the Service is through right click on My Computer -> Manage -> Services and Applications -> Services.
(3) The Performance Center Agent service must be running in Controller machine
too. Go to Controller machine and perform above step (e) to make sure that the
agent is running.
(4) When the Performance Center Agent Service starts as process on Controller
machine, an icon of Performance Center Agent will show up in Tray bar. To see
the Agent Run log, you can right click this icon and click “View Agent log”.
2. Setup on Controller machine:
a. Go to controller machine and launch the controller for a script.
b. Add a new Load Generator (Click Generators -> Add). Provide name as the local machine key name provided in the Agent Configuration in the Load Generator machine (for example: uap058_ofw).
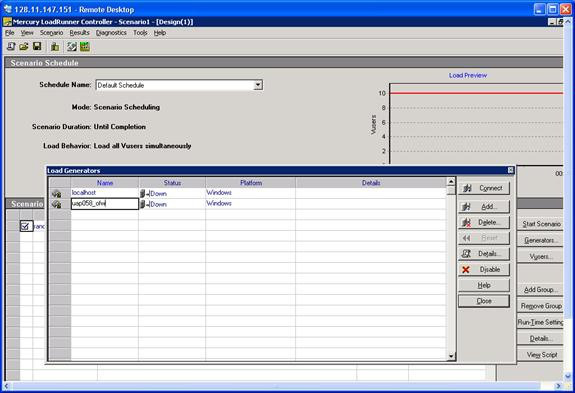
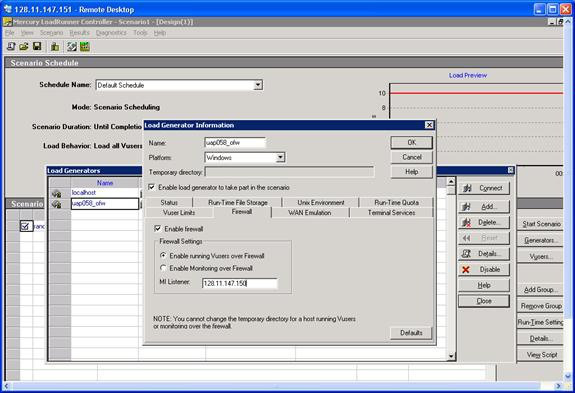
c. Highlight the agent and click on Details and go to the Firewall tab. You will see the following ‘Load Generator Information’ window:
f. For Running Vuser Over Firewall:
magentservice.exe – install
To stop LoadRunner agent as process:
magentproc.exe – remove
To start LoadRunner agent as process:
magentproc.exe – install
Note:(1) Make sure that Performance Center Agent is running by "Local System Account" (select the radio button as shown below after going to Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services -> Right Click on “Performance Center Agent” -> Click on “Log On” and then stop/start the service again from there).

(2) Make sure that the Performance Center Agent runs as Service only, so that once you logout of the Load generator machine, the LoadRunner Agent should still continue running. Also, it should be set to run as “Automatic”, so that when Load Generator machine goes down, then the Performance Center Agent should run automatically, once the machine is up. This can be verified by checking “Performance Center Agent Service” in Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services. It also shows whether the Agent Service is started/running. An alternative way to see the Service is through right click on My Computer -> Manage -> Services and Applications -> Services.
(3) The Performance Center Agent service must be running in Controller machine
too. Go to Controller machine and perform above step (e) to make sure that the
agent is running.
(4) When the Performance Center Agent Service starts as process on Controller
machine, an icon of Performance Center Agent will show up in Tray bar. To see
the Agent Run log, you can right click this icon and click “View Agent log”.
2. Setup on Controller machine:
a. Go to controller machine and launch the controller for a script.
b. Add a new Load Generator (Click Generators -> Add). Provide name as the local machine key name provided in the Agent Configuration in the Load Generator machine (for example: uap058_ofw).

c. Highlight the agent and click on Details and go to the Firewall tab. You will see the following ‘Load Generator Information’ window:

f. For Running Vuser Over Firewall:
· Check the check box for ‘Enable firewall’
· Check the button for ‘Enable running Vuser over Firewall’
· On the field for MI Listener, enter the IP address of the Controller that was configured in the Load Generator machine (step 1.(d) above).
g. Start LoadRunner agent on both ends (controller and load generator), using the commands in Step 1.(e) above.
h. Highlight the Agent and Click “Connect”.
· Check the button for ‘Enable running Vuser over Firewall’
· On the field for MI Listener, enter the IP address of the Controller that was configured in the Load Generator machine (step 1.(d) above).
g. Start LoadRunner agent on both ends (controller and load generator), using the commands in Step 1.(e) above.
h. Highlight the Agent and Click “Connect”.
Known problems and limitation:
You need to open up port 443 (bi-directional) for allowing incoming and outgoing communication on MI Listener machine.
You need to open up port 50500 between Controller and MI Listener, if the Controller and MI Listener machines are different.
Troubleshooting tips for connection issues between the MI Listener and the Agent machine
· Make sure that you do not have any Web Servers, like IIS or Oracle HTTP servers running on both the machines. These servers uses/block port 443 and will cause a problem on launching LoadRunner agent.
· To verify that port 443 is open to allow communication between these machines, go to the agent (Load Generator) machine, launch DOS prompt and type in the command ‘telnet 443’ . For example,
telnet 128.11.147.150 443
If port 443 is open then you should see a connected telnet session window. If you do not see this, check with your Network admin/Firewall group to ensure that port 443 is open or not.
· The “Performance Center Agent Service” must be running either by ‘System User account’ or by a user who has administrative privileges on this machine (Username and password details need to be provided). These details can be found by right click on the service in Start -> Settings -> Control Panel -> Administrative Tools -> Services -> Performance Center Agent Service.
Additional tips:
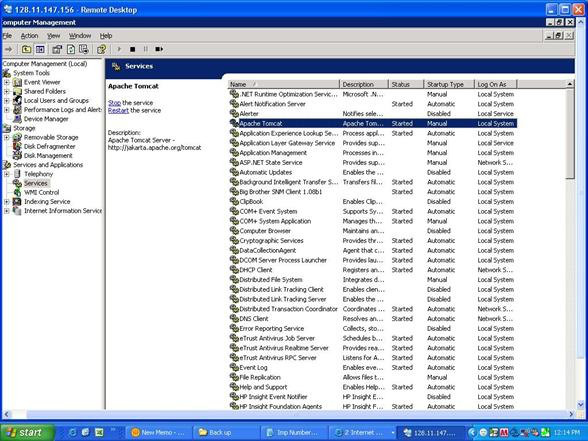
· If you see the “Page can not be displayed” error in Performance Center web page(s), then login to Performance Center Web Server box and make sure that “Apache Tomcat” service is started (as shown below).
Question – The default user id named ‘admin’ was configured to login to Performance center Load test. It is not working now.
A.1 – The first step is to make sure that the user name and password is written correctly. The password is case-sensitive.
The default administrator account is Admin, Admin for the user and password.
A.2 – The second step perform in case that the first is not working, is the following:
• Open Documents And SettingsAll UsersApplication DataMicrosoftCryptoRSAMachineKeys and delete the entry that begins with f9416f003254e610da1f9bad8e4c383_.
• Restart IIS. Choose Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services. Select IIS Admin Service and click Restart Service.